
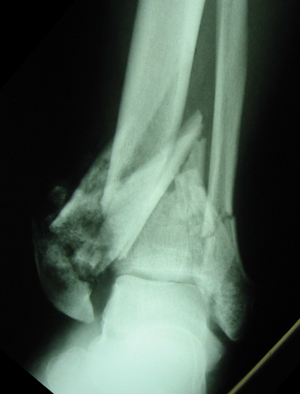
These characteristics are similar to a typical Maisonneuve fracture, which is a pronation external rotation ankle fracture. There was also inferior tibiofibular separation. In this case, the fibula fracture was long and oblique, and the fracture line was proximal to the fibula. The case presented here is a rare pattern of Maisonneuve fracture, which has the characteristics of both pronation external rotation ankle fracture and supination adduction ankle fracture. If violence persists, rupture of the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament or avulsion fracture of the posterior tibial tubercle may occur. Once injured, the medial structure is damaged first, including rupture of the deltoid ligament or fracture of the medial malleolus, followed by rupture of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament or avulsion fracture of the attachment, rupture of the interosseous ligament, rupture of the interosseous membrane, and proximal fibula fracture. Most scholars classify Maisonneuve fractures as pronation external rotation ankle fractures according to the Lauge-Hansen classification. According to the Lauge-Hansen classification, ankle fractures can be divided into four types: Supination external rotation, supination adduction, pronation external rotation and pronation abduction.

The Lauge-Hansen classification provides a sequential mechanism of injury that considers soft tissue as well as osseous structures in the development of ankle fractures. For either closed reduction or open reduction, the physician can reduce the fracture according to the opposite direction of the injury mechanism. Understanding the mechanism of injury is very important for the treatment of ankle fracture. For patients with suspected Maisonneuve fracture, full-length leg radiographs or even stress-position radiographs should be taken. Careful examination of the entire lower leg should be performed in all patients with ankle fractures. These results suggest that Maisonneuve fracture should be highly suspected in patients with simple medial malleolar fracture. Maisonneuve fracture was confirmed by careful physical examination and full-length radiographs of the lower leg. Three days after the injury, the patient was re-examined in our outpatient department due to ankle pain. The results suggested medial malleolar fracture with slight separation of the inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis. Since the patient only complained of pain in the ankle, only an ankle radiograph was performed. In this case, the patient was initially admitted to an outside hospital. Maisonneuve fracture is often missed because most patients complain of ankle pain rather than proximal fibula pain. According to the literature, Maisonneuve fractures account for approximately 7% of ankle fractures. Maisonneuve fracture was first named in 1840 by the French surgeon Maisonneuve. Intraoperative stress radiographs showed that the fracture was in good alignment and that the tibiofibular syndesmosis was stable. Finally, the anterior talofibular ligament was repaired with absorbable sutures at the lateral incision. The fracture was still fretting and was supplementally fixed with microplate screws. Next, the medial malleolar fracture was reduced by an arc-shaped incision along the posterolateral side of the medial malleolus and fixed by two 3.5-mm partially threaded cannulated screws (Figure 3). The screw placement direction was oriented 30° from posterior to anterior with slight dorsiflexion of the ankle. After satisfactory anatomical reduction by fluoroscopy, the syndesmosis was fixed with locking plate screws.
Kirschner wire was used for temporary fixation. The length of the fibula was restored, and the inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis was reduced. The inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis was separated, and the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament was ruptured. Routine disinfection, dressing, and tourniquet were performed.įirst, the inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis was explored by a lateral approach. After successful anesthesia, the patient was placed in the supine position. Meanwhile, ligament exploration and repair were performed. On the second day after admission, we performed open reduction and internal fixation of the right ankle fracture in the operating room.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
